Quote from Jacob Christian on March 1, 2023, 7:10 amSome interesting information about alloying elements in steel production.
https://www.metals-hub.com/blog/alloying-elements-in-steel-production/
Some interesting information about alloying elements in steel production.
https://www.metals-hub.com/blog/alloying-elements-in-steel-production/
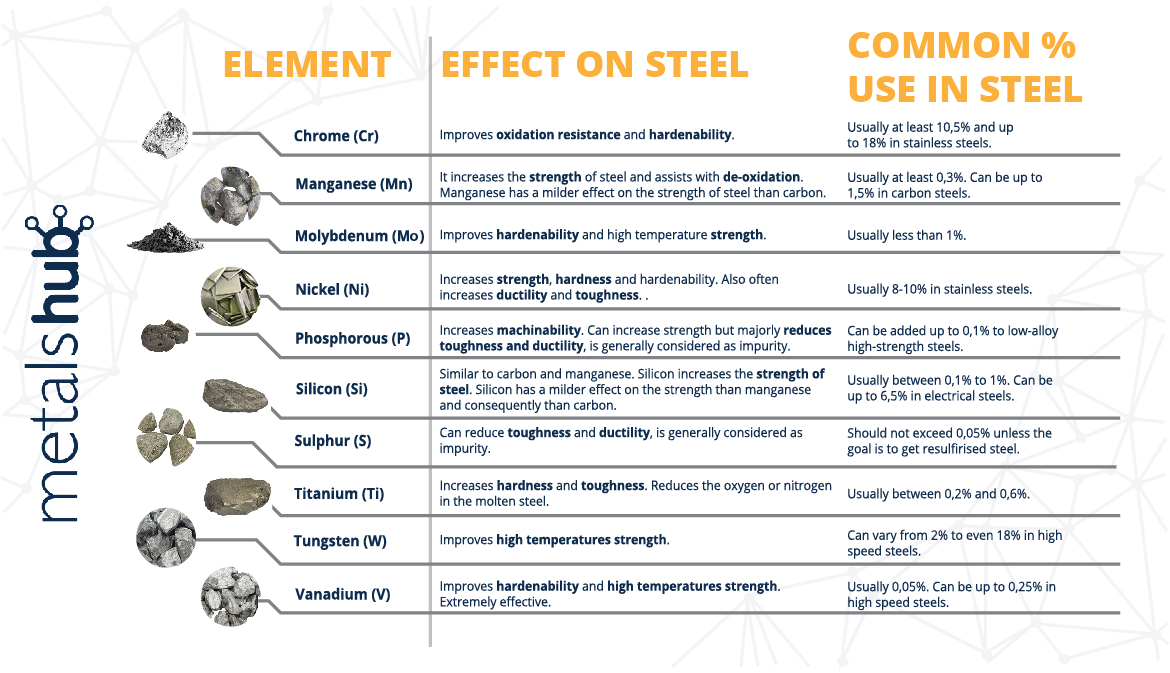
Quote from Jacob Christian on June 18, 2024, 10:58 amHere is just a little bit more information on effects of different alloying elements in high carbon steel
Alloying elements play a crucial role in modifying the properties of high carbon steel, which typically contains more than 0.6% carbon. Here are detailed effects of common alloying elements:
1. Chromium (Cr)
- Increased Hardness and Strength: Chromium increases the hardenability and strength of steel. It helps in forming carbides (Cr23C6), which contribute to hardness.
- Corrosion Resistance: Chromium significantly improves corrosion resistance by forming a passive oxide layer on the steel surface.
- Wear Resistance: Chromium carbides are very hard and contribute to excellent wear resistance.2. Manganese (Mn)
- Strength and Hardness: Manganese enhances strength and hardness by forming solid solutions and by increasing the steel's hardenability.
- Deoxidization: It acts as a deoxidizer, removing oxygen from molten steel and reducing the occurrence of defects.
- Wear Resistance: Manganese increases wear resistance, especially in the presence of high carbon content.3. Nickel (Ni)
- Toughness: Nickel enhances toughness and impact resistance, especially at low temperatures.
- Strength: It increases strength while maintaining ductility and toughness.
- Corrosion Resistance: Nickel improves resistance to corrosion and oxidation.4. Molybdenum (Mo)
- High Temperature Strength: Molybdenum enhances the strength of steel at high temperatures.
- Hardenability: It increases hardenability, allowing for deeper and more uniform hardening.
- Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride environments.5. Vanadium (V)
- Refinement of Grain Structure: Vanadium refines the grain structure of steel, which enhances toughness and strength.
- Carbide Formation: It forms vanadium carbides (V4C3), which contribute to wear resistance and hardness.
- Increased Yield Strength: Vanadium increases yield strength and tensile strength.6. Silicon (Si)
- Strength and Elasticity: Silicon increases strength and elasticity, and it also helps in deoxidization during steelmaking.
- Magnetic Properties: It improves magnetic properties and is often used in electrical steels.
- Corrosion Resistance: Silicon can enhance resistance to oxidation and scaling at high temperatures.7. Tungsten (W)
- High Temperature Strength: Tungsten provides strength and hardness at high temperatures.
- Carbide Formation: It forms tungsten carbides (WC), which are extremely hard and wear-resistant.
- Hardenability: Tungsten increases hardenability and resistance to tempering.8. Cobalt (Co)
- High Temperature Strength: Cobalt increases the hardness and strength of steel at high temperatures.
- Magnetic Properties: It enhances magnetic properties.
- Wear Resistance: Cobalt improves wear resistance and hot hardness.9. Aluminum (Al)
- Deoxidizer: Aluminum is a strong deoxidizer, improving the quality of steel.
- Nitriding: It forms aluminum nitrides (AlN), which improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Grain Refinement: Aluminum helps in refining grain structure, improving mechanical properties.10. Copper (Cu)
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper improves resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
- Strength: It can enhance the strength of steel, especially in weathering steels.11. Titanium (Ti)
- Grain Refinement: Titanium refines grain structure and improves mechanical properties.
- Carbide Formation: It forms stable titanium carbides (TiC), enhancing wear resistance.
- Prevention of Grain Growth: Titanium helps in stabilizing the grain structure, preventing excessive grain growth during heat treatment.The addition of alloying elements to high carbon steel modifies its properties, enhancing hardness, strength, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and other specific attributes depending on the alloying elements used. The careful selection and combination of these elements allow for tailoring the steel to meet specific performance requirements in various applications such as tools, machinery, automotive, and construction.
Here is just a little bit more information on effects of different alloying elements in high carbon steel
Alloying elements play a crucial role in modifying the properties of high carbon steel, which typically contains more than 0.6% carbon. Here are detailed effects of common alloying elements:
1. Chromium (Cr)
- Increased Hardness and Strength: Chromium increases the hardenability and strength of steel. It helps in forming carbides (Cr23C6), which contribute to hardness.
- Corrosion Resistance: Chromium significantly improves corrosion resistance by forming a passive oxide layer on the steel surface.
- Wear Resistance: Chromium carbides are very hard and contribute to excellent wear resistance.
2. Manganese (Mn)
- Strength and Hardness: Manganese enhances strength and hardness by forming solid solutions and by increasing the steel's hardenability.
- Deoxidization: It acts as a deoxidizer, removing oxygen from molten steel and reducing the occurrence of defects.
- Wear Resistance: Manganese increases wear resistance, especially in the presence of high carbon content.
3. Nickel (Ni)
- Toughness: Nickel enhances toughness and impact resistance, especially at low temperatures.
- Strength: It increases strength while maintaining ductility and toughness.
- Corrosion Resistance: Nickel improves resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
4. Molybdenum (Mo)
- High Temperature Strength: Molybdenum enhances the strength of steel at high temperatures.
- Hardenability: It increases hardenability, allowing for deeper and more uniform hardening.
- Corrosion Resistance: Molybdenum improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride environments.
5. Vanadium (V)
- Refinement of Grain Structure: Vanadium refines the grain structure of steel, which enhances toughness and strength.
- Carbide Formation: It forms vanadium carbides (V4C3), which contribute to wear resistance and hardness.
- Increased Yield Strength: Vanadium increases yield strength and tensile strength.
6. Silicon (Si)
- Strength and Elasticity: Silicon increases strength and elasticity, and it also helps in deoxidization during steelmaking.
- Magnetic Properties: It improves magnetic properties and is often used in electrical steels.
- Corrosion Resistance: Silicon can enhance resistance to oxidation and scaling at high temperatures.
7. Tungsten (W)
- High Temperature Strength: Tungsten provides strength and hardness at high temperatures.
- Carbide Formation: It forms tungsten carbides (WC), which are extremely hard and wear-resistant.
- Hardenability: Tungsten increases hardenability and resistance to tempering.
8. Cobalt (Co)
- High Temperature Strength: Cobalt increases the hardness and strength of steel at high temperatures.
- Magnetic Properties: It enhances magnetic properties.
- Wear Resistance: Cobalt improves wear resistance and hot hardness.
9. Aluminum (Al)
- Deoxidizer: Aluminum is a strong deoxidizer, improving the quality of steel.
- Nitriding: It forms aluminum nitrides (AlN), which improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Grain Refinement: Aluminum helps in refining grain structure, improving mechanical properties.
10. Copper (Cu)
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper improves resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
- Strength: It can enhance the strength of steel, especially in weathering steels.
11. Titanium (Ti)
- Grain Refinement: Titanium refines grain structure and improves mechanical properties.
- Carbide Formation: It forms stable titanium carbides (TiC), enhancing wear resistance.
- Prevention of Grain Growth: Titanium helps in stabilizing the grain structure, preventing excessive grain growth during heat treatment.
The addition of alloying elements to high carbon steel modifies its properties, enhancing hardness, strength, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and other specific attributes depending on the alloying elements used. The careful selection and combination of these elements allow for tailoring the steel to meet specific performance requirements in various applications such as tools, machinery, automotive, and construction.
